T-Mobile is setting out to prove that carriers don’t need to deploy extremely high-frequency mmWave technology to get blazing fast speeds. Thanks to Carrier Aggregation technology, the “Un-carrier” has demonstrated performance of 3Gbps download speeds on good old-fashioned low-band and mid-band 5G channels.
In a press release today, T-Mobile revealed that it has reached these unprecedented speeds for the first time ever on a commercial device; in this case, a Samsung Galaxy S22 powered by a Snapdragon X65 modem. “This test demonstrates the incredible power of mid-band spectrum and represents another huge step forward for stand-alone 5G,” said Neville Ray, President of Technology at T-Mobile.
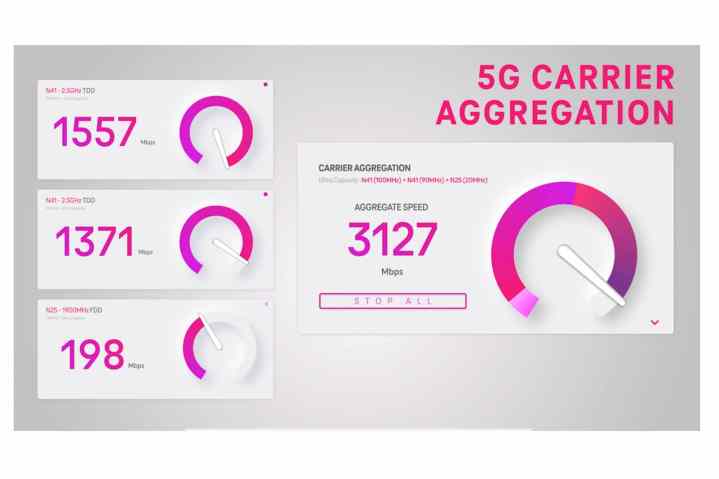
How 5G Carrier Aggregation works
It’s rare to reach even single gigabit speeds using mid-band frequencies. The recent C-band rollouts from AT&T and Verizon are improving things, and some isolated tests have shown performance peaking slightly above 1Gbps. But most customers typically find themselves in the sub-500Mbps range with this flavor of 5G.
Still, with mid-band frequencies capable of reaching 5G speeds of 1Gbps — albeit only under ideal conditions — T-Mobile set out to find out what it could accomplish by tying three of these frequencies together, using a technique known as 5G Carrier Aggregation (NR CA).

For this specific test, T-Mobile used two channels from its 2.5GHz Ultra Capacity 5G network and one channel of 1900MHz (1.9GHz) spectrum that’s typically occupied by older 4G/LTE services. This provided an effective 210MHz of 5G spectrum across the three channels.
The 1.9GHz frequencies that T-Mobile used in its testing are also part of a standalone 5G architecture (5G SA) network that T-Mobile plans to bring online later this year. Despite 4G/LTE frequencies operating in the same spectrum, this new 1.9GHz channel won’t have its performance hampered by relying on Dynamic Spectrum Sharing (DSS).
Which devices can use Carrier Aggregation
The first stage of T-Mobile’s new aggregated network went online this week, with two 2.5GHz channels to provide faster speeds and greater network capacity in key areas. The 1.9GHz 5G SA spectrum will go live later this year to add a third channel. Interestingly, the carrier adds that Samsung Galaxy S22 owners will get the first crack at this additional spectrum. However, it will eventually expand to additional areas and devices “in the near future.”
Sadly, some devices won’t be able to take advantage of these higher speeds due to a lack of support for Carrier Aggregation in their modem chipsets. The Snapdragon X60, used in Samsung’s Galaxy S21 and Apple’s iPhone 13 lineups, was the first to introduce 5G Carrier Aggregation of any kind. This means the older X55-equipped iPhone 12 and Samsung Galaxy S20 Ultra will be left out of the party.
However, even though the X60 supports NR CA, it’s limited to 200MHz of bandwidth on the sub-6GHz frequencies, slightly below the 210MHz that T-Mobile was taking advantage of in its tests. By comparison, the X65 and the more recently announced X70 both offer 300MHz of bandwidth, plus other significant performance improvements.
T-Mobile hasn’t shared which areas are covered by the new 5G NR CA capabilities. The reliance on 2.5GHz mid-band 5G means it won’t exist outside the carrier’s 5G Ultra Capacity network, but it’s likely rolling out first in more densely populated areas.



